Posts Tagged ‘Skin’
- In: Health
- 3 Comments
Hives (urticaria), also known as welts, is a common skin condition with itchy, pink to red bumps that appear and disappear anywhere on the body. An individual lesion of hives typically lasts a few hours before fading away, and new hives can appear as older areas disappear.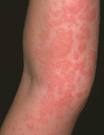
Physicians arbitrarily divide hives into acute (new or periodic episodes lasting fewer than 6 weeks) and chronic (periodic episodes lasting more than 6 weeks). Though many people have a single episode of acute hives that goes away within a few days to weeks, some individuals may have chronic hives, periodic (recurrent) attacks of hives that come over periods of years.
Hives can be triggered by many things, including:
* Medications, especially aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, narcotic painkillers, or antibiotics
* Infections with viruses, bacteria, or fungi
* Environmental allergies such as insect bites, pollen, mold, or animal dander
* Physical exposures such as heat, cold, water, sunlight, or pressure
* A medical condition such as gland diseases, blood diseases, or cancer
* Food allergies, such as strawberries, eggs, nuts, or shellfish
* Stress
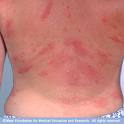 In up to 90% of outbreaks of hives, a trigger is never found despite extensive testing; these cases are referred to as idiopathic urticaria. In approximately 50% of idiopathic urticaria outbreaks, hives are most likely caused by a reaction from the person’s own immune system (autoimmune reaction).
In up to 90% of outbreaks of hives, a trigger is never found despite extensive testing; these cases are referred to as idiopathic urticaria. In approximately 50% of idiopathic urticaria outbreaks, hives are most likely caused by a reaction from the person’s own immune system (autoimmune reaction).
Lets avoid “Scabies”..
Posted on: November 12, 2008
Following are some facts on Scabies. This contagious skin disease can be a nightmare for you if you don’t take precautions. This piece of post is to lighten up the world to be healthy.
- Scabies [SKAY-bees] is a skin disease caused by a parasitic mite.
- Scabies is spread by prolonged person-to-person contact and is very contagious.
- Anyone can get scabies.
- Scabies is treatable with mite-killing skin lotions and creams.
- To prevent scabies: 1) avoid contact with people with scabies, and 2) make sure that affected persons and their contacts are treated.
What is scabies?
Scabies is a contagious mite infection of the skin.
What is the infectious agent that causes scabies?
Scabies is caused by Sarcoptes scabiei, a parasite mite.
Where is scabies found?
Scabies occurs worldwide. Scabies mites live on human blood and need the warmth of the human body to survive. Away from the body, they die within 48 hours.
How do people get scabies?
Scabies is spread from person to person mainly by prolonged (several minutes) direct skin-to-skin contact, such as touching a person who has scabies. In rare cases, scabies can spread by contact with clothes, towels, bedding, and other personal items that were recently in contact with an infected person.
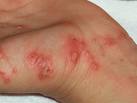
Burrowing of the mites causes the infection. Scabies mites tunnel under the skin, lay eggs, and produce substances that cause an allergic reaction. The path of a mite’s burrow looks like a line of tiny blisters on the skin. Larvae hatch from the eggs and live under the skin’s surface, where they develop into adult mites.
What are the signs and symptoms of scabies?
The earliest and most common symptom is intense itching, especially at night. An early scabies rash will show up on the skin as a line of tiny blisters or little red bumps. In more serious cases, the skin might be crusty or scaly.
In adults, signs of scabies will usually appear first in body folds — particularly between the fingers, on the elbows or wrists, on the buttocks or waistline, around the nipples for women, and on the penis for men. Scabies rarely affects the skin above the neck.
In infants and children, scabies can affect the entire body, including the palms, soles of the feet, and head and scalp. The child may be tired and cranky because of loss of sleep from itching.
How soon after exposure do symptoms appear?
It can take up to 2 to 6 weeks before a newly infected person will notice any itching or rash. Persons who have already had scabies and are re-exposed might show symptoms in 1 to 4 days.
How is scabies diagnosed?
Scabies is diagnosed by the characteristic rash. The diagnosis can be confirmed by finding mites or eggs in skin scrapings.
Who is at risk for scabies?
Anyone can get scabies. It can strike people of any age, race, or sex, regardless of personal cleanliness. Scabies is not a disease of poverty, neglect, or poor hygiene. However, it is more common among people living in crowded conditions and among those with close physical contact with others, such as children, mothers of infants, and persons in nursing homes.
What complications can result from scabies?
Scratching can cause infected sores. Some people become very sensitive to the mites and develop large areas of inflamed skin.
What is the treatment for scabies?
Treating scabies means killing the mites and their eggs. Prescription skin creams or lotions containing 5% permethrin, lindane, or crotamiton will kill the mites and eggs. Lotions must be applied according to the package directions. It can take 1 to 2 weeks after treatment for the itching to stop. A second treatment in 7 days is often recommended.
If you suspect scabies:
- See a dermatologist (skin doctor) right away for diagnosis. Remember, scabies does not indicate anything about your personal cleanliness.
- Wash and dry clothing, bed linens, and towels on the hot cycle, or have personal items professionally dry cleaned. Clothing that cannot be laundered or dry cleaned should be stored in plastic bags for several days to kill the mites.
- Vacuum rugs and furniture, and discard the vacuum bag.
- Treat all household members, personal contacts, and sexual contacts at the same time, whether or not they have symptoms.
- Do not treat scabies with home remedies. These can make the condition worse. Do not use steroids or other creams unless prescribed by a doctor.
How common is scabies?
Scabies is a fairly common infectious disease that occurs sporadically and also sometimes in outbreaks. Most outbreaks occur in nursing homes, institutions, and child-care centers.
Is scabies an emerging infectious disease?
Yes. There has been a recent wave of infestation in the United States. Scabies in residents of nursing homes and extended care facilities has become a common problem.
How can scabies be prevented?
- Avoid physical contact with infected persons and their belongings, especially clothing and bedding.
- Treat all family and household members who had skin contact with an infected person, whether or not they are itching or have a rash.
- Exclude persons with scabies from school or day care until 24 hours after treatment.
This fact sheet is for information only and is not meant to be used for self-diagnosis or as a substitute for consultation with a health-care provider. If you have any questions about the disease described above or think that you might have a parasitic infection, consult a health-care provider.
Source : http://www.dhpe.org/infect